| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 알고리즘
- 파이썬
- 카카오 코테
- AWS
- 구조체배열
- 컴포넌트스캔
- C언어
- @Autowired
- Nodejs
- 가상면접사례로배우는대규모시스템설계기초
- 코테
- 카카오 알고리즘
- 프로그래머스
- OpenCV
- 카카오
- nestjs typeorm
- 해시
- spring boot
- thymeleaf
- TypeORM
- 스프링
- nestJS
- C++
- Spring
- @Component
- python
- 시스템호출
- git
- 코딩테스트
- nestjs auth
Archives
- Today
- Total
공부 기록장 💻
[자료구조] 스택(Stack) - 연결 리스트로 구현한 스택 구조 (Stack using Linked List) 본문
# CS Study/DS Algorithm
[자료구조] 스택(Stack) - 연결 리스트로 구현한 스택 구조 (Stack using Linked List)
dream_for 2021. 5. 10. 00:55
연결리스트에서 head가 가리키는 값에 새로운 노드를 추가하는 구조와 스택 구조는 매우 유사하다.
첫 부분에 노드를 추가하는 (insert_first) 연결 리스트와 구조가 유사하며 top을 가리키는 포인터가 있다는 것만 조금 다르다.



// 연결리스트를 이용한 스택 구조
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int StackObject;
// Object에 대한 structure과 object를 담은 스택
typedef struct StackRec {
StackObject item; // 데이터필드
struct StackRec* link; // 링크필드 : next item의 주소를 담은 포인터
}StackRec;
// link 포인터를 따라가며 가장 마지막에 삽ㅇ비한 StackRec의 Object를 가리키는 포인터 구조체
typedef struct StackTop { // StackRec1->StackRec2->StackRect3
StackRec* top; // 마지막 레코드를 가리키는 포인터
}StackTop;
// init isempty isfull(x) push pop peek
// 스택 초기화 (top값을 -1로 설정)
void initialize(StackTop* s) {
s->top = NULL; // 스택의 데이터가 아직 없으므로, NULL값을 가지는 top포인터
}
// 스택이 비어 있는지 검사하는 함수
int isEmpty(StackTop* s) { return (s->top == NULL); } // s->top이 NULL이면 TRUE 반환
// 스택에 요소를 삽입하는 함수
void push(StackTop* s, StackObject item) {
// 메모리 할당 (임시 포인터 변수)
StackRec* temp = (StackRec*)malloc(sizeof(StackRec));
if (temp == NULL) {
printf("memory allocation failure \n");
}
else {
temp->item = item;
temp->link = s->top; // 새로운 item의 링크는 기존 top이 가리키던 링크를
s->top = temp; // 기존 top은 temp가 됨
}
}
StackObject pop(StackTop* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) {
printf("stack is empty \n");
}
else {
// 임시 포인터변수 temp에 top 저장
StackRec* temp = s->top;
int item = temp->item;
s->top = s->top->link; // s->top이 가리키던 것을 top에 저장
free(temp); // s->top을 저장한 temp에 대하여 메모리 해제
return item;
}
}
// print out stack
void printStack(StackTop* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) return;
StackRec* temp = s->top;
for (;temp;temp = temp->link) // temp가 NULL이 아닌 동안에
{
printf("| < %d > ", temp->item);
}
printf("|\n\n");
}
// clear the stack
void clear(StackTop* s) {
StackRec* temp = s->top;
StackRec* removed;
while (temp) {
removed = temp; // 삭제할 요소를 removed에 대입
temp = temp->link; // temp는 next포인터를 따라감
printf("remove < %d > \n", removed->item);
free(removed);
}
s->top = temp; // s->top을 temp(마지막값)으로 업데이트
}
int main() {
StackTop s1;
initialize(&s1);
push(&s1, 15);
push(&s1, 62);
push(&s1, 35);
push(&s1, 52);
push(&s1, 37);
push(&s1, 55);
printf("\n-- [ Print ] --\n");
printStack(&s1);
printf("\n-- [ Clear Stack ] --\n");
clear(&s1);
printf("\n-- [ Print ] --\n");
printStack(&s1);
}
추가 구현 : 학생 구조체 정보 스택 연결 리스트 활용

// 연결리스트를 이용한 스택 구조
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 스택 오브젝트 - 학생의 학번, 이름 구조체
typedef struct {
int number;
char name[10];
}StackObject;
typedef struct StackRec {
StackObject item; // 데이터필드
struct StackRec* link; // 링크필드
}StackRec;
typedef struct StackTop { // StackRec1->StackRec2->StackRect3
StackRec* top; // 마지막으로 저장된 StackRect을 가리키는 포인터
}StackTop;
// init isempty isfull(x) push pop peek
// 스택 초기화 (top값을 NULL로 설정)
void initialize(StackTop* s) {
s->top = NULL;
}
int isEmpty(StackTop* s) { return (s->top == NULL); } // s->top이 NULL이면 TRUE 반환
// 요소 삽입
void push(StackTop* s, StackObject item) {
// 메모리 할당 (임시 포인터 변수)
StackRec* temp = (StackRec*)malloc(sizeof(StackRec));
if (temp == NULL) {
printf("memory allocation failure \n");
}
else {
temp->item = item;
temp->link = s->top; // 새로운 item의 링크는 기존 top이 가리키던 링크를
s->top = temp; // 기존 top은 temp가 됨
}
}
// 요소 pop
StackObject pop(StackTop* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) {
printf("stack is empty \n");
}
else {
// 임시 포인터변수 temp에 top 저장
StackRec* temp = s->top;
StackObject item = temp->item;
s->top = s->top->link; // s->top이 가리키던 것을 top에 저장
free(temp); // s->top을 저장한 temp에 대하여 메모리 해제
return item;
}
}
// print out stack
void printStack(StackTop* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) return;
StackRec* temp = s->top;
for (;temp;temp = temp->link) // temp가 NULL이 아닌 동안에
{
printf("| < %d %s > ", temp->item.number, temp->item.name);
}
printf("|\n\n");
}
// clear the stack
void clear(StackTop* s) {
StackRec* temp = s->top;
StackRec* removed;
while (temp) {
removed = temp; // 삭제할 요소를 removed에 대입
temp = temp->link; // temp는 next포인터를 따라감
printf("remove < %d %s > \n", removed->item.number, removed->item.name);
free(removed);
}
s->top = temp; // s->top을 temp(마지막값)으로 업데이트
}
int main() {
FILE* fp;
StackTop s1;
StackObject tempItem; // 파일로부터 읽은 데이터를 임시로 저장
int nTemp;
char name[10];
initialize(&s1);
fp = fopen("studData.txt", "rt");
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "file not open\n");
exit(1);
}
while (!feof(fp)) {
fscanf(fp, "%d %s", &tempItem.number, tempItem.name);
push(&s1, tempItem);
}
printf("\n-- [ Print ] --\n");
printStack(&s1);
printf("\n-- [ Clear Stack ] --\n");
clear(&s1);
printf("\n-- [ Print ] --\n");
printStack(&s1);
fclose(fp);
}

< Debugging - 로컬창 히스토리 >를 살펴보자
LILF의 과정을 살펴볼 수 있다.
initialize (s->top=NULL)

push
item push(1 홍길동)
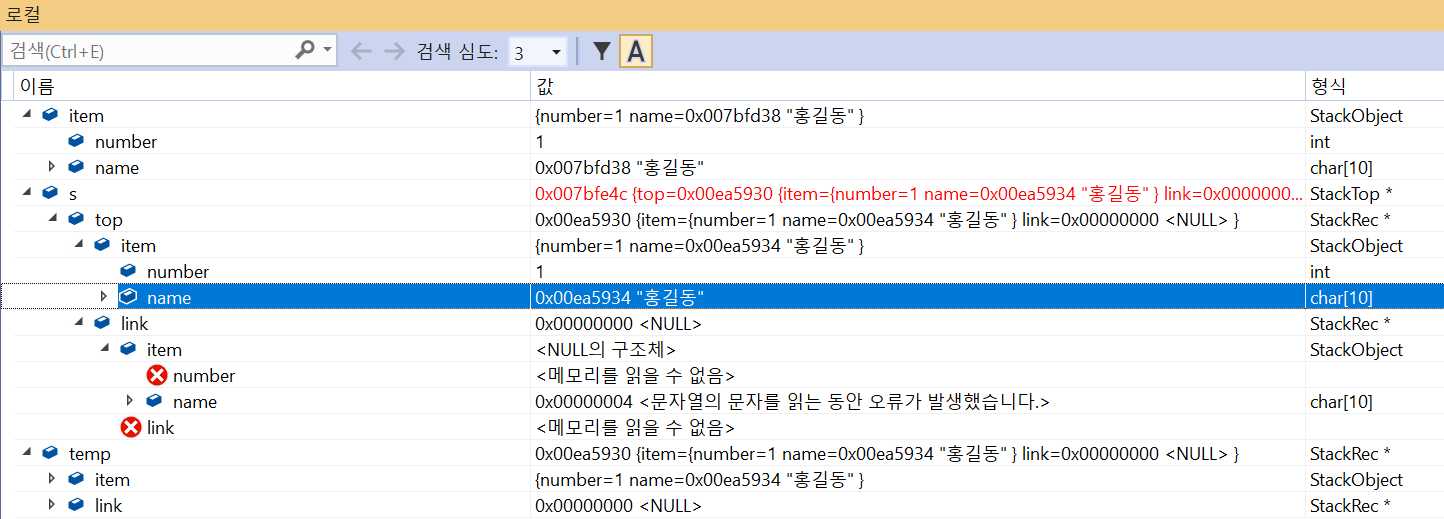
item push(2 이순신)

printStack

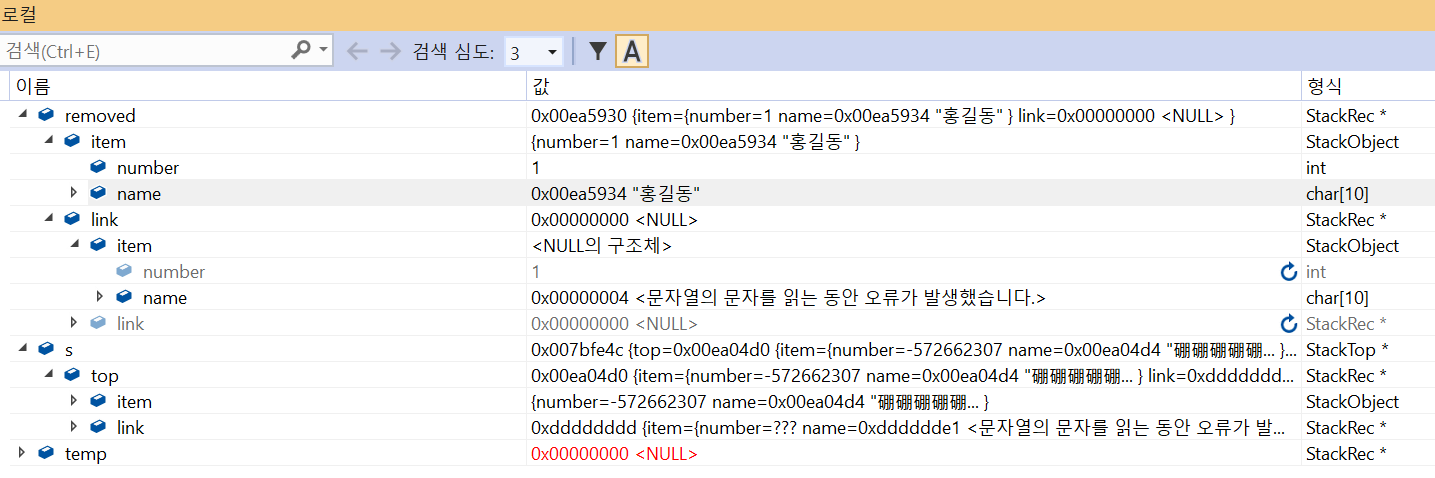
clear Stack
removed : 3 김유신

removed : 2 이순신

removed : 1 홍길동
728x90
반응형
'# CS Study > DS Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 큐(Queue)의 구조와 구현 - 선형 큐(Linear Queue)와 원형 큐(Circular Queue) (0) | 2021.05.20 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 스택(Stack) 응용 - 미로 탐색 프로그램 (0) | 2021.05.20 |
| [자료구조] 스택 (stack) - 후위 표기 수식 계산(postfix expression evaluation), 중위 표기 수식을 후위 표기로의 변환 (0) | 2021.05.07 |
| [자료구조] 스택 활용 - 괄호 검사 프로그램 ( Check Balanced Parentheses Using Stack) (0) | 2021.05.04 |
| [자료구조] 스택(stack)의 구조와 구현 (0) | 2021.05.03 |
Comments
