| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 파이썬
- 가상면접사례로배우는대규모시스템설계기초
- 카카오 코테
- @Autowired
- Spring
- 컴포넌트스캔
- 구조체배열
- 코테
- 프로그래머스
- C++
- 시스템호출
- 알고리즘
- thymeleaf
- spring boot
- Nodejs
- TypeORM
- C언어
- 해시
- nestjs auth
- OpenCV
- 카카오 알고리즘
- 코딩테스트
- nestJS
- nestjs typeorm
- @Component
- 스프링
- git
- 카카오
- AWS
- python
Archives
- Today
- Total
공부 기록장 💻
명품 C++ Programming 2장 실습 문제 - C++ 표준 입출력, cin, cout, string 객체, getline 함수 본문
# Language & Tools/C++
명품 C++ Programming 2장 실습 문제 - C++ 표준 입출력, cin, cout, string 객체, getline 함수
dream_for 2021. 3. 18. 13:17(명품 C++ 프로그래밍 2장)
4.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
double n[5];
double max;
cout << "5개의 실수를 입력하라 >> ";
for (int i = 0;i < 5;i++) {
cin >> n[i];
if (i == 0)max = n[i];
if (n[i] > max)max = n[i];
}
cout << "가장 큰 수는 " << max << endl;
}
5.
cin.getline() - cin 객체의 멤버 함수 사용
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[100];
char find;
int cnt = 0;
cout << "문자들을 입력하라(100개 미만)." << endl;
cin.getline(str, 100);
cout << "찾으려는 문자 입력 : ";
cin >> find;
for (int i = 0;i < strlen(str);i++)
if (str[i] == find) cnt++;
cout << find << "의 개수는 " << cnt << endl;
}

8.
스트링 객체 string 문자열을 입력 받기(delimitChar = ',' 문자 만날 때 까지)
- getline() 은 스트링 객체를 입력 받기 위해 <string> 헤더 파일에 선언된 전역 함수이다.
- <enter>키가 입력되기 전까지 입력 스트림 버퍼에 입력된 문자열이 저장된다.
- <enter>키가 입력되고 난 후, 반복문에 의해 [ getline() 함수에서 cin 버퍼로부터 name 객체 한 개 읽기, cout 스트림 객체, if()문 ] 이 총 5번 실행된다.
- i=0 -> getline 실행 - "Mozart"가 name에 저장 => cout 실행 - "1 : Mozart" 출력 => if문 실행
- i=1 -> getline 실행 - "Elvis Presley"가 name에 저장 => cout 실행 - "2 : Elvis Presley" 출력 => if문 실행
- ...
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string name;
string longName;
int len = 0;
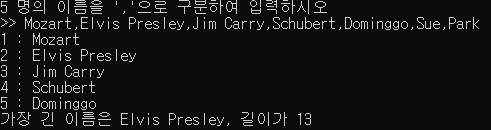
cout << "5 명의 이름을 ','으로 구분하여 입력하시오"<<endl<<">> ";
for (int i = 0;i < 5;i++) {
getline(cin, name, ',');
cout << i + 1 << " : " << name<<endl;
if (name.length() > len) {
len = name.length();
longName = name;
}
}
cout << "가장 긴 이름은 " << longName << ", 길이가 " << len << endl;
}
15.
다른 수많은 방법이 있긴 하지만,
목적과 힌트에서 '공백을 포함하는 문자열'을 읽고
공백 문자를 찾아 연산자와 두 개의 피연산자를 구분하여 계산하라 명시되어 있기 때문에
조금은 어려운 방법을 택해보았다.
stoi() 함수를 이용하여 발견되는 첫번째 정수를 n1에 저장한다.
공백을 찾아 발견한 위치를 index에 저장하고, index+1부터 시작되는 문자열에 대한 서브스트링을 sub에 저장한다.
sub에서 stoi() 를 이용해 n2 두번째 피연산자를 저장한다.
// 공백을 포함하는 문자열 입력 받아 연산자, 두 개의 피연산자 구분
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
char op;
int n1, n2, res;
cout<<"종료는 exit 입력하기"<<endl;
while (1)
{
cout << "? ";
getline(cin, s);
if (s == "exit")break;
int index = 0;
index = s.find(' '); // 첫번째 공백 문자 찾은 위치를 index에 저장
n1 = stoi(s); // 공백 앞은 피연산자
char op = s[index + 1]; // 공백 뒤는 연산자
//printf("index = %d, op = %c \n", index, s[index - 1]);
index =(s, index+1); // index+1 부터 다시 공백 찾기
string sub = s.substr(index + 1);
n2 = stoi(sub);
//printf("index = %d, n2= %c \n", index, s[index + 1]);
switch (op) {
case '+':res = n1 + n2;break;
case '-':res = n1 - n2;break;
case '*':res = n1 * n2;break;
case '/':res = n1 / n2;break;
default:break;
}
cout << n1<<' '<<op<<' '<<n2<<" = " << res << endl;
}
}

728x90
반응형
'# Language & Tools > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C/C++] 문자열 처리 함수 c_str(), atoi(), stoi() (0) | 2021.04.09 |
|---|---|
| [C++] string 클래스 - string 문자열 객체 동적 생성, string 멤버 함수 사용 (0) | 2021.04.07 |
| [C++] 클래스와 객체 - 클래스 선언부/구현부, 생성자, 소멸자, 멤버 접근 지정자, 자동 인라인함수, 구조체 (0) | 2021.04.06 |
| [C++] 문자열 입력 - <cstring> cin.getline, <string> - getline (0) | 2021.04.06 |
| [C/C++] C++ 프로그래밍 기본 (0) | 2021.03.17 |
Comments
